

The stability of a fibula fracture determines treatment. Open wounds should be cleaned and dressed in a sterile manner.Fracture dislocations should be reduced.Site of tenderness (palpate entire length of fibula).
LATERAL MALLEOLUS OF FIBULA SKIN
The skin should be assessed for any open injuries and the amount of soft tissues swelling.ĭislocations should be reduced and casted immediately. Neurovascular status should be carefully examined. From weight bearing with an antalgic gait to non-weight bearing with significant pain, swelling, discomfort and varying deformity. This type of injury includes Maisonneuve injuries.īased on foot position at time of injury and the force applied through the foot.
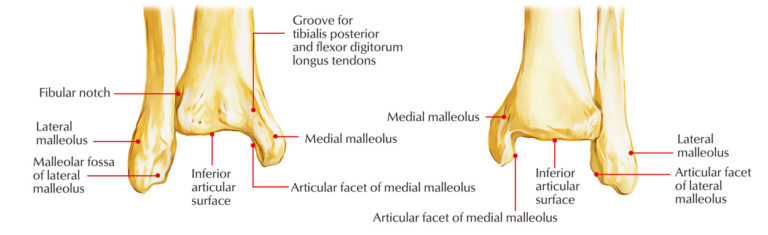
Causes disruption of the syndesmosis and is usually associated with medial ankle injuries. Weber C - a fracture above the level of the syndesmosis. May be associated with medial ankle injury/fracture or posterior malleolus fractures. Mechanism is external rotation of the foot. Weber B - a fracture at or near the level of the syndesmosis. Weber A - a fibular fracture below the level of the syndesmosis. Higher risk of syndesmotic disruption and instability is associated with more proximal fractures. Orthopaedic review either in ED or within 1-3 days.īased on the position of the fibular fracture. Reduction if required, short leg backslab, NWBĭisplaced/>25% of articular surface: short leg backslab, NWB Talar shift or medial malleolar fracture: reduction, short leg backslab Orthopaedic follow-up in ED or within 1-2 daysįibula fracture above syndesmosis (Weber C)Īnkle in normal anatomical position: short leg backslab NWB Weber B, displaced: short leg backslab, NWB Weber B, undisplaced: short leg backslab NWB


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
